Food, Global Health Reading time 3 min
Artificial intelligence to improve the control of infectious diseases in animals
Published on 20 February 2020

For the past 15 years, the Joint Research Unit for Biology, Epidemiology and Risk Analysis (BIOEPAR), a member of the France Futur Elevage Carnot Institute, has been specialised in modelling the spread of animal diseases. Its models are able to define and evaluate strategies for the management of health risks and their costs to livestock farms within a defined geographical area. Combining computer simulations and the integration of data from the field, these models constitute a valuable tool for the sector in a particularly competitive and tense economic environment.
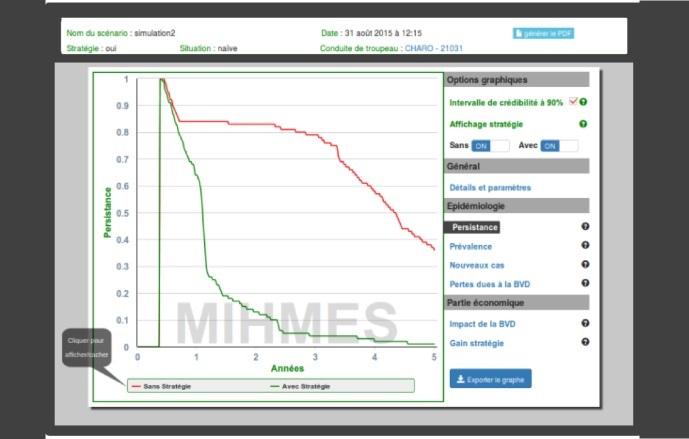
In the context of the MIHMES (2012-2017) Investments for the Future project, coordinated by BIOEPAR, scientists from INRA and INRIA developed new modelling methods that combine the technologies of artificial intelligence and of the cloud. They have produced decision-support tools (DST) based on the framework environments created during this project. The first framework, Diffuse (Distributed Framework for Cloud-Based Epidemic Simulations), is able to exploit all the resources in the cloud for the distribution of calculations and thus enable gains in performance and execution time. The second, Emulsion (Epidemiological Multi-Level Simulation), uses artificial intelligence (multi-agent, multi-level system) and can accelerate and ensure the reliability of the development of DST and new epidemiological models. Together, these innovations can facilitate the integration of biological knowledge on livestock practices and health measures (hygiene, animal movements, characteristics of vaccines, etc.). They also permit the study of as many scenarios as necessary, from the herd scale to that of a region, sector or even country.
EvalBVD and EvalParaTuB: DSTs that are already available and have been welcomed by professionals
The scientists notably developed two tools that received awards at the Salon International de l’Elevage (SPACE) in 2015 and 2016: EvalBVD to manage bovine viral diarrhoea, and EvalParaTuB to manage Johne’s disease. These DSTs are intended for use by veterinarians and health authorities. They enable the development of strategies to manage these diseases at the scale of a farm, to compare them and evaluate their economic impact. These tools can be accessed via the web, users having a personal space which provides back up of the scenarios tested.
An open consortium to maintain the technology and develop new DSTs

These DSTs, software systems and frameworks have proved their worth in terms of reliability and robustness. Valorisation of these results is ongoing in the context of a consortium that will enable industrialisation of the development process for new software systems and DSTs for use in animal health. This consortium, STEMAH (Software and Tools for Epidemiological Modelling in Animal Health) already involves partners from the MIHMES project. It aims to maintain existing applications, broaden them to larger scales and propose a coherent software suite that integrates DSTs to manage other health issues (vaccination, control plans, etc.).
The France Futur Elevage Carnot Institute is supporting the scientists in assembling and constituting the STEMAH consortium, which is open to any interested public or private sector actors who can join it at any time.
The MIHMES project : Multi-scale modelling, from animal Intra-Host to Metapopulation, of mechanisms of pathogen spread to Evaluate control Strategies (2012-2017) - produced scientific knowledge and methods to aid in the management of enzootic infectious animal diseases and risks in veterinary public health.
6 laboratories were involved: five French research teams and one from Sweden. Their skills extend from mathematics and computer sciences to economics, alongside infectiology, immunology, and epidemiology.
The overall cost was €6 million, with €1.2 million funded by the French government’s Investments for the Future programme (National Research Agency) and €621,000 provided by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) covering the Pays-de-la-Loire region.
France Futur Élevage

The France Futur Élevage Carnot Institute can offer companies in the livestock sector its skills in R&D which mobilise three essential levers to ensure multi-performance, sustainable and profitable livestock farming: health, diet and livestock systems, and animal genetics.
France Futur Élevage unites actors in agricultural and veterinary research with a global reputation and expert know-how in R&D from three Agricultural Technical Institutes that are international leaders in services to livestock. Each year, it funds its partner teams for several upstream (revitalisation) projects which aim to generate results that can be transferred to industry.
Twitter : @Carnot_F2E
Contact : Fanny Wacquet, chargée d'affaires, fanny.wacquet@inrae.fr ;Tél : 01 42 75 93 26
Inra Transfert, 28 rue du Docteur Finaly, 75015 Paris
| The France Futur Élevage network: | Key figures : |
|---|---|
|
1 000 research scientists and engineers |
386 research contracts with 238 private sector actors |
